What does -(2) mean in UNIT MEASURES
-(2) is a mathematical expression that indicates a negative value squared. It is commonly used in algebra, calculus, and other areas of mathematics.
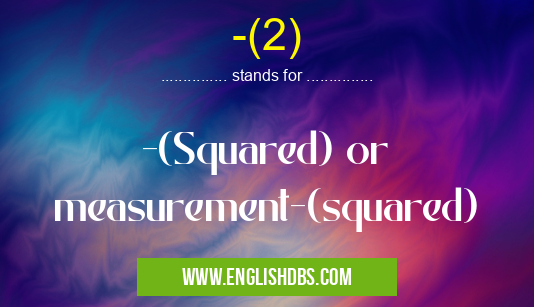
-(2) meaning in Unit Measures in Miscellaneous
-(2) mostly used in an acronym Unit Measures in Category Miscellaneous that means -(Squared) or measurement-(squared)
Shorthand: -(2),
Full Form: -(Squared) or measurement-(squared)
For more information of "-(Squared) or measurement-(squared)", see the section below.
Understanding -(2)
-(2) can be written as -1 multiplied by the square of the number. For example, -(2) = -1 * 2^2 = -4.
Mathematical Operations
When working with -(2), it is important to remember the following mathematical operations:
- Multiplication: If -(2) is multiplied by any number, the result will be negative.
- Division: If -(2) is divided by any number, the result will be negative if the divisor is positive and positive if the divisor is negative.
- Exponents: If -(2) is raised to any exponent, the result will be negative if the exponent is odd and positive if the exponent is even.
Applications
-(2) has various applications in mathematics, including:
- Solving Equations: It is used to solve equations that involve quadratic terms, such as x^2 + 2x - 3 = 0.
- Graphing Functions: It is used to graph functions that have negative quadratic terms, such as the parabola y = -x^2.
- Physics: It is used in physics to describe the acceleration of objects under the influence of gravity.
Essential Questions and Answers on -(Squared) or measurement-(squared) in "MISCELLANEOUS»UNITMEASURES"
What does -(2) mean?
-(2) represents a measurement squared. For instance, if the measurement is 5, then -(2) would be 5 x 5 = 25.
Final Words: Understanding -(2) is essential for solving various mathematical problems and applications. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics that represents a negative value squared and undergoes specific mathematical operations.
